Online payments have rapidly become a preferred payment method in many countries worldwide. Alongside this trend, the demand for authentication and security has never been higher, aiming to protect transactions from increasingly sophisticated threats, ensure absolute safety, and maintain a seamless user experience.
Over the past decade, the world has witnessed a powerful surge in e-commerce, smartphones, and high-speed connectivity infrastructure. Cashless payment habits have become an integral part of daily life. Bank cards, digital wallets, Apple Pay, Google Pay, QR codes, and cross-border payment platforms like Alipay+, WeChat Pay (China), and UPI (India) are used daily by millions for shopping, bill payments, and personal financial transactions.
However, alongside this growth comes a downside: increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. Cybersecurity reports highlight a significant rise in advanced attack methods, from phishing scams and malware on mobile devices to OTP theft, creating an urgent need for financial service providers, banks, and payment organizations to enhance authentication and transaction security measures.
Popular Authentication Methods Today
Currently, many countries employ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), which applies at least two of three factors: Something you have (e.g., a device or OTP), Something you know (e.g., a password or PIN), and Something you are (e.g., biometric data like fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans).
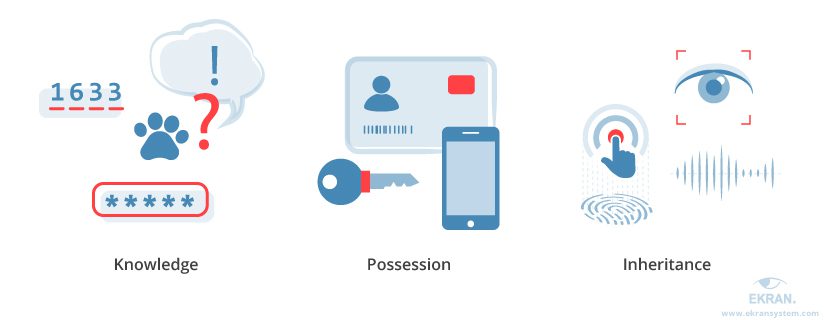
For example, in India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mandates two-factor authentication (2FA) for all online transactions, typically combining OTP with a PIN. In the UAE, OTPs delivered via SMS or email are a common authentication method for financial transactions. However, OTPs and PINs are increasingly vulnerable, becoming prime targets for cyberattacks, paving the way for new, more secure, and efficient authentication trends.
Trends in Online Payment Security
Biometrics is considered a significant advancement in authentication security today. When a user registers, their device generates a pair of security keys: a private key stored on the device, unlocked only through biometric authentication, and a public key stored on the payment network. During a transaction, the device signs the request with the private key, the network verifies it with the public key, and the result is sent to the bank. This process shifts authentication from the bank to the payment network or a third party, reducing the risk of OTP theft and providing a smoother user experience.

In addition to biometrics, securing payment applications on mobile devices is another critical piece of the security puzzle. For instance, Google Play Protect, Android’s default security layer, can scan apps and detect known malware at the operating system level. However, it lacks the ability to identify sophisticated in-app fraud, such as fake keyboards, unauthorized access, or zero-day attacks. Advanced app-level security solutions enable real-time detection and response to threats, from blocking suspicious transactions to adjusting security policies based on the usage environment.
As online payments continue to thrive, biometrics and mobile payment protection technologies are emerging as inevitable trends, strengthening transaction security, reducing cyber risks, and delivering a seamless, reliable payment experience. This marks a significant step toward a future where every online transaction is comprehensively protected, providing absolute peace of mind for both users and businesses.






